Create cert
First, we shall create a root CA cert.
Note: you shall be promoted for Country Name, Organization Name, Common Name, etc. There fields refer to the identity of the root CA we are creating, not the actual domain.
mkdir mycertcd mycertopenssl genrsa -des3 -out rootCA.key 2048openssl req -x509 -new -nodes -key rootCA.key -sha256 -days 1024 -out rootCA.pemUse the rootCA to create private key for your domain. You can store private key at /etc/nginx/ssl/ or /etc/ssl/private/.
Note: Most import field is Common Name (e.g. server FQDN or YOUR name), where you use localhost or a fake domain name (e.g. www.mydomain.dev or www.mydomain.test). Don't include a challenge password. I shall use www.mydomain.test for my example.
sudo openssl req -new -sha256 -nodes -out server.csr -newkey rsa:2048 -keyout /etc/nginx/ssl/mydomain.keyCreate a v3.ext file.
authorityKeyIdentifier=keyid,issuer
basicConstraints=CA:FALSE
keyUsage = digitalSignature, nonRepudiation, keyEncipherment, dataEncipherment
subjectAltName = @alt_names
[alt_names]
DNS.1 = www.mydomain.testCreate your cert. You can store your cert at /etc/nginx/ssl/ or /etc/ssl/certs/.
sudo openssl x509 -req -in server.csr -CA rootCA.pem -CAkey rootCA.key -CAcreateserial -out /etc/nginx/ssl/mydomain.crt -days 1000 -sha256 -extfile v3.extConfigure nginx SSL
Assuming you already install and setup Nginx.
Edit you Nginx configuration file. Refer to // EDIT: for editing.
erver {
listen 80;
// EDIT: listen to both port 80 and ssl
listen 443 ssl;
// EDIT: make sure domain name is correct
server_name www.mydomain.test;
ssl_certificate /etc/nginx/ssl/mydomain.crt;
ssl_certificate_key /etc/nginx/ssl/mydomain.key;Restart nginx.
sudo service nginx restartEdit the /etc/hosts file to create a localhost entry for our fake domain www.mydomain.test.
sudo nano /etc/hosts27.0.0.1 www.mydomain.testTest if the page can be accessed using HTTPS at https://www.mydomain.test/.
Chrome will probably complaint of Your connection is not private / ERR_CERT_AUTHORITY_INVALID, where you can proceed by clicking on ADVANCE and click on Proceed to ... (unsafe).
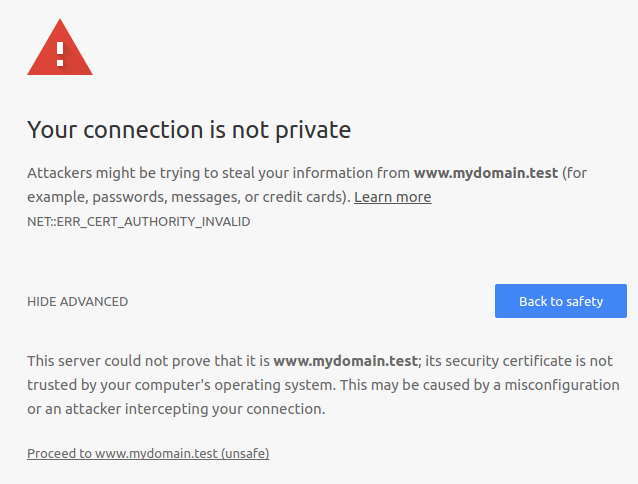
Cofigure Chrome to accept out rootCA as Trusted Authority
Access chrome://settings/certificates in Chrome or Settings -> Advanced -> Manage certificates -> AUTHRORITIES.
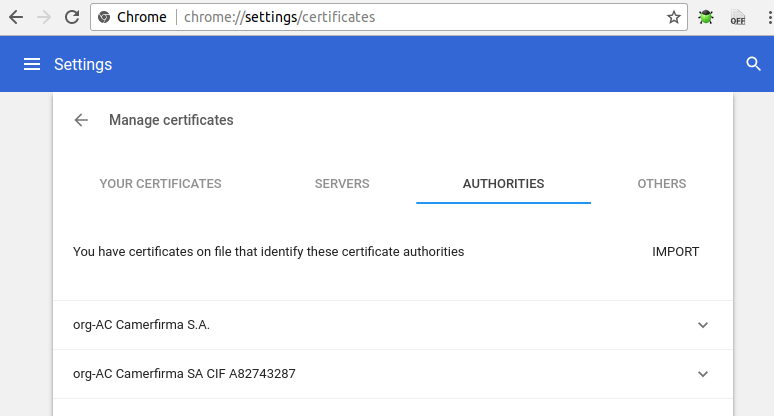
Click IMPORT, and select mycert/rootCA.pem created earlier.
When promoted, select Trust this certificate for identifying websites.

Try accessing https://www.mydomain.test/ again and chrome no longer
Import Chrome Trusted Authority Cert using command line
If you dislike import CA certificate using GUI, you can use a command line tool.
Install libnss3-tools / certutil.
sudo apt-get install libnss3-toolsImport our rootCA.
certutil -d sql:$HOME/.pki/nssdb -A -t "CT,c,c" -n "Test Authority - /mycert/rootCA.pem" -i /mycert/rootCA.pemCheck if import is successful.
certutil -d sql:$HOME/.pki/nssdb -L